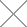Can Plastic Plugs Be Used in Explosion Proof Zones
In hazardous areas prone to fire and explosion within chemical plants, it’s common practice to use flameproof electrical equipment to effectively control sparks and prevent flammable gases from entering the electrical equipment and causing flash explosion accidents. There’s debate on whether explosion-proof plugs can be made of plastic such as PVC. Many instruments come with plastic plugs as standard, while some are metal. So, is it imperative for plugs to be made of metal? Can plastic plugs be used in explosion-proof areas?
Can Explosion-proof Sealing Components Be Made of Plastic Materials?
According to GB/T 3836 requirements, explosion-proof plugs are considered Ex equipment sealing components. These are tested separately from the equipment’s housing but possess an Ex equipment explosion-proof certificate, intended to be installed on the housing of Ex equipment (as per Article 3.29 of GB/T 3836.1-2021).

The purpose is to prevent parts that could ignite explosive gas environments from being housed internally, withstand the pressure generated by the explosion of internal explosive mixtures, and prevent the explosion from propagating to the surrounding explosive gas environment (Article 3.1 of GB/T 3836.2-2021).
While metal plugs are commonly used in explosion-proof areas due to their superior explosion-proof properties, but they have high costs. If the material quality is not qualified, they may fail, compromising safety. However, in certain specialized applications where corrosion or other factors may cause erosion or deformation, materials like plastic and rubber, known for their corrosion resistance, can still be applicable in explosion-proof areas post-certification.
It’s crucial to emphasize that replacing metal components with plastic parts must adhere to relevant safety standards and specifications. Acquiring explosion-proof certification for plastic plugs is challenging, hence their limited usage in practical applications. If plastic explosion-proof plugs are required, considerations must be made regarding their application environment, durability, strength, etc., and they must undergo relevant explosion-proof certification to verify compliance with safety standards.
In summary, there’s no prohibition against using plastic plugs in explosion-proof areas, as long as they meet explosion-proof requirements and obtain corresponding certification.
In accordance with Article 16.4 of GB/T 3836.1-2021, plugs must meet the following requirements:
Sealing components used to seal redundant holes on the housing wall of electrical equipment must comply with the requirements of the corresponding specialized explosion-proof type. These sealing components should only be removable with tools.
Threaded sealing components should be Ex equipment sealing components, Ex components, or part of a complete equipment explosion-proof certificate.
- Class I non-threaded sealing components should be Ex equipment sealing components, Ex components, or part of a complete equipment explosion-proof certificate.
- Class II or Class III non-threaded sealing components should be Ex components or part of a complete equipment explosion-proof certificate.
In conclusion: there’s no specification prohibiting the use of plastic plugs. However, in the market, apart from being part of a complete equipment explosion-proof certificate, plastic explosion-proof plugs are only available as increased safety plugs.
Note:Generally speaking, the materials for explosion-proof plugs are primarily limited to metal materials such as galvanized carbon steel, nickel-plated brass, stainless steel, etc.
How to Properly Differentiate Between Explosion-proof Plugs and Fasteners?
Explosion-proof plugs seal redundant cable openings on explosion-proof electrical equipment, whereas fasteners are used to operate one or more threaded fasteners (screws, double-end bolts, bolts, or nuts) to open or close doors or covers (Article 3.12 of GB/T 3836.2-2021).
Fasteners typically secure explosion-proof box doors and are not permitted to be made of plastic materials or light alloy fasteners (Article 11.1 of GB/T 3836.2-2021). In other words, plastic parts are not allowed for bolts or screws connecting explosion-proof boxes. This should not be confused with the prohibition of using plastic materials for explosion-proof plugs.
What are Explosion-proof Plugs and Sealing Components?
Explosion-proof Plugs: These are sealing components tested separately from the equipment’s housing but possess an Ex equipment explosion-proof certificate, intended to be installed on the housing of Ex equipment (Article 3.16 of GB/T 3836.2-2021).
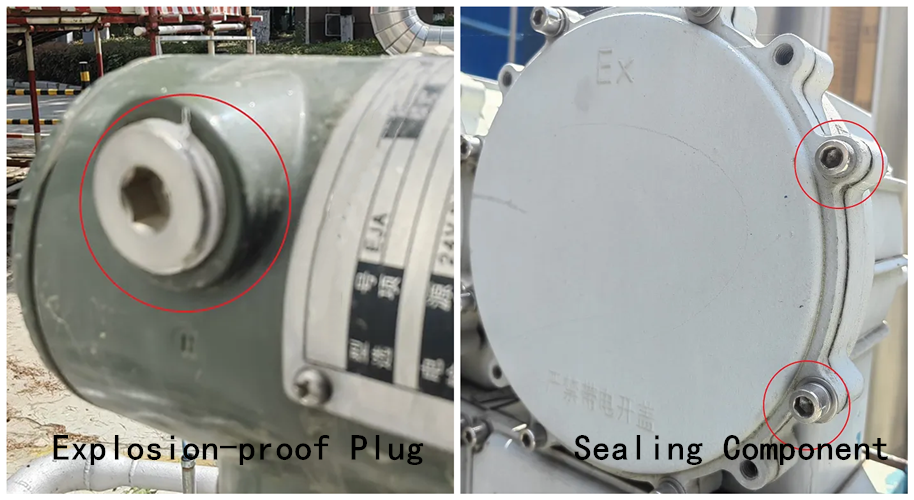
Sealing Components: If the introduced hole on the explosion-proof enclosure is not frequently used, a sealing component shall be used to seal it to maintain the explosion-proof performance of the enclosure (Article 13.8 of GB/T 3836.2-2021).
Holykell also recommends you using explosion-proof measuring instrument in industrial flammable and explosive occasions. Contact us for professional technical instructions.